The Faculty of Applied Sciences of Macao Polytechnic University has made new breakthroughs in the field of intelligent molecular generation, advancing the Drug Discovery Process
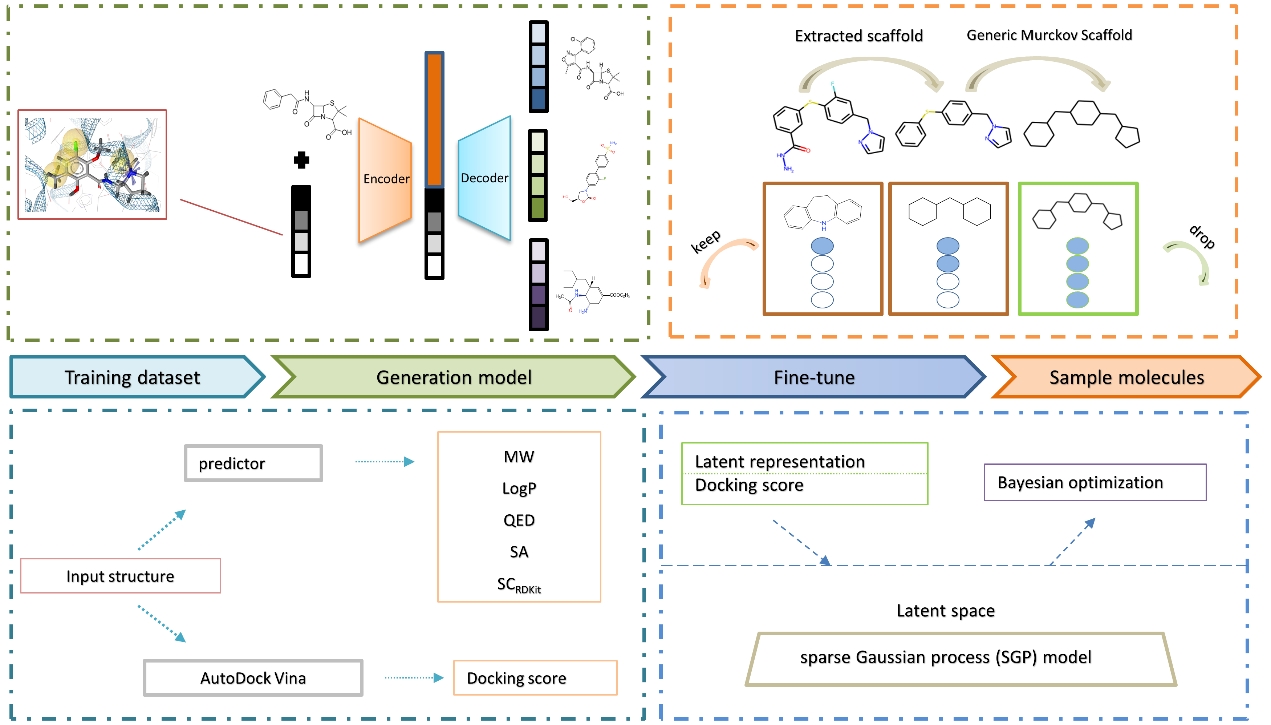
The research paper titled "Deep Generation Model Guided by the Docking Score for Active Molecular Design" authored by Professor Liu Huanxiang's team and Professor Yao Xiaojun's team, from the Faculty of Applied Sciences at Macao Polytechnic University, has been published in "Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling", which is the international authoritative academic journal in the field of chemical informatics and artificial intelligence research. This paper presents a new molecular generation model called COMG, developed through collaboration between the two professor teams. The method utilizes docking scores and pharmacophore information as constraints for molecular generation, enabling the creation of new molecules with desired properties. The authors applied the developed model to generate candidate active molecules for several targets, demonstrating the effectiveness of the model. The model significantly enhances the quality of generated molecules, including their activity and drug-likeness, thereby improving the efficiency of drug discovery, shortening the drug development cycle, and reducing research costs.
The approach employs a ligand-centric generation model that matches the pharmacophores of active compounds to iteratively search the entire chemical space, selecting compounds with higher affinity for the target. The molecular generation model is primarily constructed based on a multi-objective conditional variational autoencoder, which simultaneously constrains synthesizability, drug-likeness, and other relevant physicochemical properties during the search process in chemical space, thereby increasing the potential of generated molecules. Molecular docking guides compound optimization, combining docking scores with Bayesian optimization for model fine-tuning, resulting in potential candidate molecules with high affinity for specific targets. During the fine-tuning process, the model also incorporates a similarity scaffold filter, aiding in obtaining more diverse molecular structures during chemical space exploration.
In comparison to primarily docking score-guided generation models, the generated molecules show significant improvements across various molecular properties. Furthermore, by using the COMG model, the authors generated multiple potential active druglike molecules targeting three different types of targets—DRD3, HPK1, and PPAR-γ. These molecules exhibited excellent performance on multiple evaluation metrics, indicating their potential for further research.
Since its establishment in 2022, the Centre for Artificial Intelligence Drug Discovery at the Faculty of Applied Sciences, Macao Polytechnic University, has been actively promoting the interdisciplinary integration of AI technology with pharmacy, chemistry, biology, and other fields. The centre also launched Macao's first doctoral program in AI drug discovery, aiming to nurture interdisciplinary talents capable of utilizing AI technology for new drug development. Additionally, the centre organizes a series of academic exchange activities, collaborates with various research institutions and universities, and actively promotes the organic integration of research achievements and industrial applications, contributing to the pharmaceutical industry.